How Boeing can come again from disaster
 BBC
BBCThis has been a depressing yr for Boeing. Not solely has it struggled to deal with a security and high quality management disaster, it has misplaced billions of {dollars} following a strike by staff that paralysed manufacturing at two of its greatest factories.
Even its house programme has been in hassle. Two astronauts had been left stranded on the Worldwide Area Station in June after their Boeing Starliner capsule developed a possible fault, which might have made returning to Earth in it too harmful.
On high of all this, the corporate faces a disaster of confidence from inside its personal ranks, says Bjorn Fehrm, an aeronautical and financial analyst at business consultants Leeham Firm.
“Individuals in Boeing do not consider in phrases from high administration any extra,” he says.
 Reuters
ReutersSam Mohawk is a 51-year-old high quality assurance investigator at Boeing’s manufacturing facility in Renton close to Seattle, an enormous plant the place the 737 Max is constructed. It’s the firm’s best-selling plane, however one with a chequered security file.
Earlier this yr Mr Mohawk got here ahead as a whistleblower, claiming that chaos on the manufacturing facility ground within the years because the Covid-19 pandemic had led to 1000’s of defective or “non-conforming” components going lacking, and probably being fitted aboard plane which have since been despatched to clients.
“The entire system was simply in shambles,” he says of that interval. “It [had] form of simply damaged down.”
His allegations got here to mild in June once they had been referred to throughout a congressional listening to in Washington DC into security failures on the aerospace large.
Through the session, Boeing’s high bosses had been accused by Republican Senator Josh Hawley of “strip-mining” the corporate for revenue and chopping corners on security with the intention to increase earnings.
David Calhoun, who was Boeing’s chief government on the time, mentioned he “did not recognise” Mr Hawley’s depiction of the corporate. “That’s not the way in which we function,” Mr Calhoun mentioned again then. “I’m happy with each motion we’ve taken.”
 Getty Pictures
Getty PicturesSince then, Boeing has appointed a brand new chief government, Kelly Ortberg, who has pledged to “restore belief” within the enterprise, overhaul its company tradition and prioritise the security of passengers. The corporate can also be within the means of implementing a complete security and high quality plan, which was launched earlier within the yr.
However in keeping with Mr Mohawk, who nonetheless works at Boeing, the drive to construct planes as rapidly as doable with the intention to maximise revenues stays. The accountants, he insists, are “100%” working the operation.
“Nothing has modified,” says Mr Mohawk. “Our executives speak to the press and say, ‘high quality and security is our primary precedence’. However it’s simply the identical.”
Boeing rejects Mr Mohawk’s claims. It insists they’ve been completely investigated and that none of them had been discovered to be legitimate.
In a press release, it mentioned: “Boeing knowledge methods do observe components, together with non-conforming components. The investigations into Mr Mohawk’s claims discovered no proof that faulty components had been put in on Boeing planes, and not one of the points raised affected security.”
 Alamy
AlamyOne other Boeing worker referred to as Nathan (not his actual title), who works within the firm’s Everett manufacturing facility in Washington state, the place the 777 is constructed, describes low employees morale and corners being minimize on the manufacturing line. Staff “do not all the time observe the principles as a result of they really feel the stress from their supervisor, and so they don’t seem to be taking steps to make sure their very own security”, he claims.
However Mike Dunlop, an aerospace business veteran and creator of a e book about turning round failing companies, argues that Boeing has in truth already begun the method of reworking itself by going again to fundamentals.
He believes lots of Boeing’s issues consequence from the conceitedness of the corporate’s administration up to now, because it sought to chop prices in an effort to earn more money. Lately, he says, there have been some enhancements.
“I’ve seen the most important adjustments within the firm because the Sixties. What Kelly Ortberg is doing is focusing again on their core ideas, which is to construct airplanes as successfully and safely as doable, and be a dependable provider to the airways.”
Arguably, the market wants Boeing to be wholesome. It stays an enormous firm, using greater than 150,000 individuals immediately, and numerous extra in provide chains around the globe. It’s a vital contributor to the US financial system.
However some insiders argue that it now has a credibility downside and desires to revive confidence.
Crashes and the 737 Max
Boeing’s difficult yr started on 5 January with a routine night flight from Portland Worldwide Airport in Oregon to Ontario, California. The aircraft, a brand-new Boeing 737 Max operated by Alaska Airways, had taken off minutes earlier and was climbing when one thing went badly mistaken.
“Er, yeah, we might wish to go down,” a feminine voice mentioned over the radio because the disaster erupted at 16,000ft. “Alaska 1282 declaring an emergency… we’re descending to 10,000… we’re depressurised.”
 Reuters
ReutersMoments earlier on the flight deck, First Officer Emily Wiprud had been exchanging routine messages with air site visitors management, then there was a loud bang, a sudden rush of wind and her radio headset was torn off. Air stress within the plane plummeted, as did the temperature.
Ms Wiprud and the captain hurriedly placed on oxygen masks, then labored along with calm urgency to carry the broken plane to the bottom.
What had occurred was deeply disturbing. A panel fitted over an unused emergency exit had not been bolted into place correctly and had come away because the aircraft was climbing, in keeping with the Nationwide Transportation Security Board, which investigated the incident.
The passengers had been nonetheless strapped in and nobody was critically damage. However as investigators identified, it may have been a lot worse.
What made the incident stand out was the truth that the 737 Max was Boeing’s latest plane and its bestselling mannequin in historical past.
Since its entry into service, greater than 1,600 have been despatched to airways and an extra 4,800 are on order. However even earlier than this, its security file was tarnished.
 European Pressphoto Company
European Pressphoto CompanyIn late 2018, an plane went down within the sea off the coast of Indonesia. 4 months later one other aircraft crashed minutes after take-off from Advertdis Ababa in Ethiopia. A complete of 346 individuals had been killed.
Each accidents had been in the end blamed on a poorly designed piece of flight management software program. This had been fitted to handle dealing with quirks on the brand new aircraft, and forestall pilots, who had been used to earlier variations of the 737, from needing costly retraining.
In apply, it turned energetic on the mistaken time, and compelled each plane into catastrophic dives, in keeping with investigators.
Did price chopping ‘jeopardise security’?
Some critics blame these accidents on a concentrate on the underside line on the expense of security. In a press release, The Basis for Aviation Security, which is chaired by ex-Boeing whistleblower Ed Pierson, mentioned: “Consideration to share worth and revenue margins alone has confirmed to be a flawed technique.”
Within the aftermath of these crashes, the 737 Max was grounded for 20 months as regulators examined each facet of its design.
The corporate confronted criticism over its company tradition. A congressional report launched in September 2020 discovered that Boeing’s rush to construct new plane as rapidly as doable whereas chopping prices had “jeopardised the security of the flying public” – though its findings had been described as “partisan” by one main Republican.
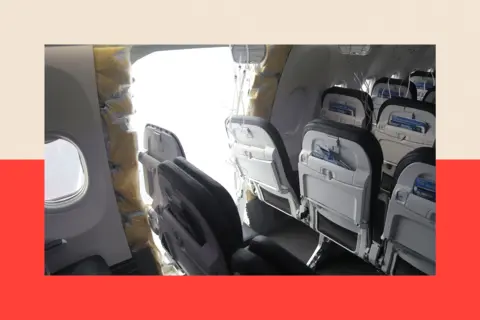 EPA
EPAThe incident in Portland, nonetheless, was the results of the failure by Boeing engineers to bolt the door panel again on correctly, after it had been eliminated to restore manufacturing flaws. But it positioned the corporate within the highlight once more.
Particularly, it drew consideration to a sequence of continuous high quality issues that had been occurring behind the scenes on the aircraft-maker and at its foremost provider Spirit AeroSystems, which makes quite a few massive plane parts together with the principle physique.
These included manufacturing defects affecting components of fuselages, tail and rudder assemblies, in addition to sealants utilized as safety towards the impact of lightning strikes in central gas tanks.
However the incident additionally positioned a renewed concentrate on claims made by whistleblowers from inside each firms, who had prompt that the stress from Boeing to provide plane rapidly, and ramp up manufacturing, had compromised security on each the 737 and 787 programmes.
 EPA
EPAThe sudden deaths of two different whistleblowers – John Barnett, who had labored in Boeing’s 787 manufacturing facility in South Carolina, and Josh Dean, who had been employed by Spirit – generated additional headlines in 2024. It resulted in pushing the broader story about Boeing as soon as once more into the information.
US politicians made their emotions clear. Richard Blumenthal, head of the Senate subcommittee on investigations mentioned: “Boeing has put income and pace of manufacturing forward of high quality and security, and in the end, that failing is on the core of its present difficulties.”
The strike that ‘price Boeing $5.5 billion’
After the Portland incident, Boeing was ordered by the US Division of Transportation to provide a complete motion plan “to handle its systemic high quality management and manufacturing points”.
The aerospace large responded by publishing an in depth technique geared toward bettering its manufacturing methods, gaining extra management over its provide chain, and inspiring staff to talk up on security and high quality management points.
It additionally promised to strengthen its coaching programmes and overhaul crucial processes on the manufacturing line.
 Reuters
ReutersOn 1 July, Boeing reached an settlement to take management of Spirit as a part of its efforts to resolve high quality issues.
There have been additionally adjustments on the high of the corporate when Mr Calhoun, who had grow to be chief government a yr after the incidents in Indonesia and Ethiopia, stepped down and was changed in August by Mr Ortberg, a veteran engineer who had spent many years within the business.
However weeks after his appointment, Boeing confronted additional disaster when greater than 30,000 unionised staff – most of them within the firm’s Washington State heartlands – went on strike over a brand new four-year contract, and the way a lot Boeing would enhance pay and different advantages for its staff.
The walkout, which started in September and lasted for seven weeks, held up manufacturing of the 737 Max, the 777 and the 767 freighter.
 Getty Pictures
Getty PicturesPreviously, the corporate had grow to be accustomed to negotiating from a place of energy, solely this time it was in a weak place, and in keeping with Bjorn Fehrm, staff had been out for revenge.
“It was apparent to them that the outdated administration had principally screwed them. That was the sentiment. They had been completely disgusted with how they’d been handled within the outdated contract,” he explains.
The consequence was a bitter dispute, at a time when the corporate was attempting to instil a brand new working tradition, and Mr Ortberg had promised to “reset” relations with its staff.
Boeing needed to dig deep to provide you with a deal that glad their calls for, which included a 38% pay rise over 4 years. In line with consultants Anderson Financial Group, the strike price the corporate greater than $5.5 billion.
Airbus versus Boeing: the fallout
All of this got here at a time when the aerospace large was already struggling financially. Within the first 9 months of 2024 it racked up losses of practically $8bn (£6.3bn). Because of this, it set out plans to chop 17,000 jobs, or a tenth of its workforce.
Boeing’s issues have taken a heavy toll on its enterprise. The place as soon as it went toe to toe with its European rival Airbus, it has now delivered fewer plane in every of the previous 5 years.
Within the first 9 months of 2024 it distributed 291 planes to its clients, whereas Airbus offered 497, in keeping with Forecast Worldwide.
For its clients, this has been irritating. Ryanair, one of many greatest patrons of the 737 Max, has minimize its progress forecasts for subsequent yr. Within the US, Southwest Airways has needed to make job cuts.
 Reuters
ReutersBut Airbus just isn’t able to take full benefit of this. Its personal order books are full to bursting, with a backlog of practically 8,700 planes. Like its rival, it has skilled issues with suppliers, resulting in delays.
In the meantime, airways need new planes. Estimates from each Boeing and Airbus recommend greater than 40,000 new plane might be wanted over the following twenty years.
The present era of plane are way more environment friendly and cheaper to run than their predecessors. So delays in renewing their fleets will price airways cash – probably resulting in increased ticket costs for his or her passengers – in addition to hampering efforts to enhance their environmental efficiency.
In line with Mr Fehrm, all this creates a gap for a 3rd participant to take a stake out there. “Over the following 5 to 10 years there might be a spot between what the market is asking for and what Airbus and Boeing can ship by 1000’s of plane.
“So it is open for a 3rd participant. Brazilian producer Embraer is a candidate. Or it will be an opportunity for Comac, the Chinese language provider, to return into completely different markets and say, ‘Really, we will do an honest job right here.'”
A ‘borderline miraculous’ revival?
In early December Mike Whitaker, administrator of the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), visited the manufacturing facility in Renton close to Seattle that Mr Mohawk has raised considerations about. On the time, Mr Whitaker mentioned: “What’s really wanted is a elementary cultural shift that is oriented round security, high quality enchancment and efficient worker engagement and coaching.
“As anticipated, Boeing has made progress executing its complete plan in these areas, and we are going to proceed to carefully monitor the outcomes as they start to ramp up manufacturing following the strike.”
However for a lot of consultants, the issues at Boeing return many years – and are unlikely to be solved in a single day.
“The toughest factor to alter in massive firms is the mindset of individuals,” says Mr Fehrm. “It takes time, and it must be manifested in actions, doing issues in another way.
“There are adjustments coming, however individuals will not have a look at what the highest administration beneath Kelly Ortberg say. They are going to search for actions.”
 Reuters
ReutersSome observers consider Mr Ortberg has a chance now to enhance the corporate’s fortunes. Mr Dunlop thinks a change in mindset might be elementary to Boeing’s future.
“The quickest approach to flip round an organization is to have a whole change in perspective on the way you deal with your staff, the way you deal with your clients, and most significantly in the way you deal with your suppliers.”
A whole reversal of its earlier method may produce a “borderline miraculous” revival, he believes.
However others are much less assured. Captain Dennis Tajer, the lead spokesman for the Allied Pilots Affiliation (the pilots’ union for American Airways), believes actual change at Boeing has to return, not from the boardroom, however from additional down the corporate’s ranks.
“The answer is beneath senior administration,” he argues.
“It is on the center administration stage, the place you discover the gatekeepers and the individuals who help doing issues correctly, not simply conserving the schedule going.”
The stakes, he insists, couldn’t be increased.
Prime picture credit score: Alamy
BBC InDepth is the brand new residence on the web site and app for the most effective evaluation and experience from our high journalists. Beneath a particular new model, we’ll carry you recent views that problem assumptions, and deep reporting on the most important points that can assist you make sense of a fancy world. And we’ll be showcasing thought-provoking content material from throughout BBC Sounds and iPlayer too. We’re beginning small however pondering massive, and we need to know what you suppose – you may ship us your suggestions by clicking on the button beneath.




&w=1200&resize=1200,0&ssl=1)
