How personal corporations are arming our forces | India Information – The Instances of India

Operation Sindoor has spotlighted India’s evolving navy capabilities, revealing the emergence of a strong personal defence sector central to the nation’s safety.A decade in the past, public sector undertakings and imported know-how dominated India’s defence narrative. In the present day, the personal sector drives innovation, not merely filling gaps. Firms akin to Tata Superior Methods (TAS), Alpha Design Applied sciences (ADTL), Paras Defence & House Applied sciences, ideaForge, and IG Drones have transitioned from being area of interest gamers to vital companions in delivering cutting-edge methods for contemporary warfare.
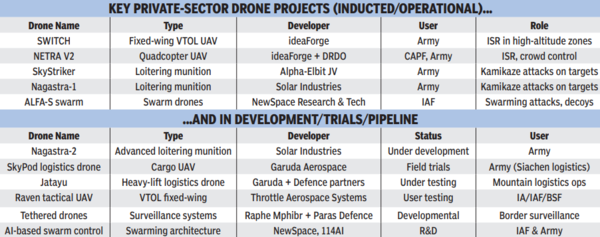
Listing of drones and different particulars
Pvt push to defenceTAS, with its legacy in aerospace and defence integration, presents complete options, together with radars, missiles and UAV methods, for Indian navy. In collaboration with Airbus Spain, it produces the C-295 navy transport plane at India’s first personal navy plane plant in Vadodara, Gujarat. Paras Defence — recognised for its credentials in indigenous design, improvement and manufacturing — units benchmarks in digital warfare, optics and drones. Equally, Alpha Design supplies a spread of methods from radars to tank elements and satellite tv for pc payloads.Different conglomerates like Larsen & Toubro (L&T), Adani Group, and Bharat Forge have considerably expanded their defence portfolios. L&T secured contracts price Rs 13,369 crore for high-powered radar methods and close-in weapons methods. Adani Defence & Aerospace inaugurated two ammunition and missile-manufacturing amenities within the UP defence hall, aiming to supply 150 million rounds of small-calibre ammunition yearly and assembly 25% of India’s requirement.It’s a d(r)one factor The personal sector’s affect is most seen in drone know-how. India’s navy drone journey started within the Nineties with Israeli UAVs such because the IAI Searcher and Heron. Recognising their strategic worth, India began to construct its personal capabilities. The Kargil Warfare in 1999 highlighted the necessity for real-time intelligence, prompting DRDO and personal corporations to speed up UAV improvement.Lower to Might 2025 and the Indian armed forces now function a rising fleet of UAVs, with many extra in improvement. Operation Sindoor underscored the central function of indigenous drones, pushed by personal corporations, in India’s navy doctrine overlaying tactical and high-altitude intel and reconnaissance platforms. ideaForge’s SWITCH UAV and NETRA V2 quadcopter, co-developed with DRDO, has entered service. Alpha Design’s partnership with Israel’s Elbit Methods produced superior methods just like the SkyStriker loitering munition, enabling precision strikes throughout Operation Sindoor. Photo voltaic Industries’ Nagastra-1 bolstered India’s tactical strike choices, whereas NewSpace Analysis & Applied sciences delivered drone-swarm capabilities to IAF.Within the pipeline The event pipeline contains logistics-focused platforms akin to Garuda Aerospace’s Jatayu, a heavy-lift drone, and SkyPod for high-altitude resupply in terrains like Siachen. Tactical drones, akin to Throttle Aerospace’s Raven and AI-driven swarm management methods from NewSpace and 114AI exhibit how Indian startups are shaping defence tendencies.The Drone Federation of India, representing over 550 firms and 5,500 pilots, has constructed this ecosystem. It goals to have India as a world drone hub by 2030. IG Drones underlines how the brand new wave of defence tech corporations are specialising in R&D, manufacturing and companies. Its collaborations with the Military and different govt our bodies combine personal experience into defence planning and execution.India’s defence exports reached practically Rs 24,000 crore ($2.9 billion) in FY25, with personal corporations enjoying a central function. Govt’s goal of Rs 50,000 crore in exports by 2029 is determined by sustained personal sector progress. The Indian drone market alone is projected to succeed in $11 billion by 2030, accounting for over 12% of the worldwide share, signalling alternatives for personal corporations and strengthening nationwide safety.Earlier this month, defence shares, each private and non-private, rallied by as much as 4% after PM Narendra Modi, referencing Operation Sindoor, known as for larger navy self-reliance. “We now have confirmed our dominance in new-age warfare,” he said. “We should lead in defence innovation by means of indigenous know-how.”Operation Sindoor’s success resulted from coverage adjustments supporting personal defence manufacturing. Since 2021, the ban on imported drones and the Manufacturing Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, with a Rs 120-crore outlay, turbocharged native innovation. Indigenous defence manufacturing reached Rs 1.3 lakh crore in FY24, with a rising share going to personal gamers. Programmes like iDEX (Improvements for Defence Excellence) and SRIJAN (for import substitution) opened doorways for each startups and established corporations.Past Operation Sindoor The personal sector’s function continues to evolve, with the longer term specializing in autonomous, AI-driven methods the place personal firms excel in expertise and agility. Operation Sindoor demonstrated that the fusion of personal innovation, public sector help, and navy imaginative and prescient allows India to say itself as a high-tech navy energy. House-based capabilities will probably be a key element of this future. Though India lags the US and China in navy satellites, it’s transferring forward with corporations like Digantara (area situational consciousness), Pixxel (Earth commentary), Dhruva House (satellites and floor methods), and Ananth Applied sciences creating key capabilities.Earlier this 12 months, three personal corporations based mostly in South India have been picked to co-develop 31 satellites underneath the House-Primarily based Surveillance-3 (SBS-3) programme, marking the primary time personal gamers are constructing satellites for strategic use. This third section of the programme, constructing on earlier Cartosat and Risat launches, will improve India’s area surveillance capability with 52 satellites in GEO (geostationary) and LEO (low Earth orbit). Isro will develop 21, whereas the personal sector will ship 31.




